The Remarkable Abilities of ButterfliesButterflies, with their delicate wings and graceful flight, have captivated human imagination for centuries. These enchanting insects possess an array of fascinating abilities that make them truly extraordinary creatures. From their unique sensory perception to their incredible transformations, butterflies showcase nature’s ingenuity in remarkable ways.
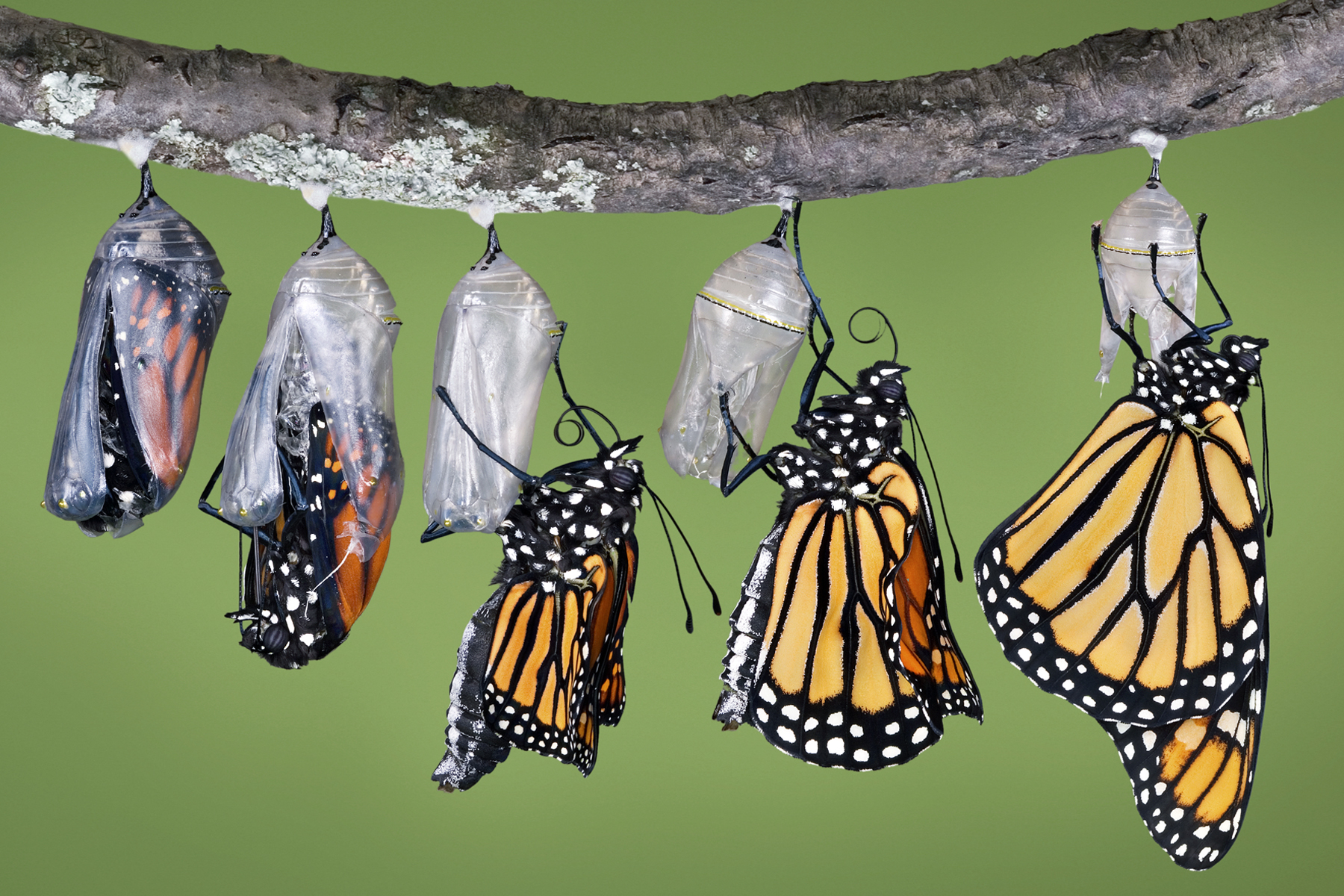




What are some unique defense mechanisms butterflies use
Butterflies have evolved a variety of fascinating defense mechanisms to protect themselves from predators. Here are some of the most unique and effective strategies they employ:
Warning Coloration (Aposematism)
Many butterflies use bright, contrasting colors as a warning signal to predators that they are toxic or unpalatable. This is known as aposematic coloration. For example:
- The monarch butterfly has striking orange and black wings that serve as a warning of its toxicity.
- Other species like the tiger moth mimic the appearance of wasps to deter predators.
Chemical Defenses
Some butterflies sequester toxic chemicals from the plants they eat as caterpillars and retain these toxins into adulthood:
- Monarch caterpillars feed on milkweed plants, ingesting cardiac glycosides that make them poisonous to many predators.
- The toxins are retained in the adult butterfly, making them unpalatable to birds and other predators.
Mimicry
Certain butterfly species have evolved to mimic the appearance of other toxic or dangerous species, even when they themselves are harmless:
- The viceroy butterfly mimics the toxic monarch, gaining protection through this resemblance.
- Some butterflies mimic the patterns and colors of wasps or other stinging insects.
Camouflage
Many butterflies use camouflage to blend in with their surroundings and avoid detection:
- Some species resemble dead leaves when their wings are closed.
- Others have patterns that help them blend into bark, foliage, or flowers.
Eyespots
Some butterflies have evolved large eyespots on their wings that can startle or confuse predators:
- These eyespots may mimic the eyes of larger animals like owls or snakes.
- They can also direct predator attacks away from vital body parts.
Transparency
Certain butterfly species have evolved transparent or partially transparent wings:
- This can make them harder for predators to spot.
- Transparency may also serve as a warning signal in some species.
Behavioral Defenses
Butterflies also use various behaviors to evade predators:
- Many species are fast, erratic flyers, making them difficult to catch.
- Some butterflies engage in “puddling” behavior, gathering in groups for safety in numbers.
- Certain species roost in groups, providing collective protection against predators.
Structural Adaptations
Some butterflies have physical adaptations that aid in their defense:
- Hairstreak butterflies have small tails on their hindwings that resemble antennae, tricking predators into attacking the wrong end.
- Some species have thickened wing veins or scales that can help them escape if grabbed by a predator.
These diverse defense mechanisms showcase the remarkable adaptability of butterflies and their evolutionary responses to predation pressures. By employing a combination of visual, chemical, and behavioral strategies, butterflies have developed sophisticated ways to survive in a world full of potential threats.
Sensory Superpowers
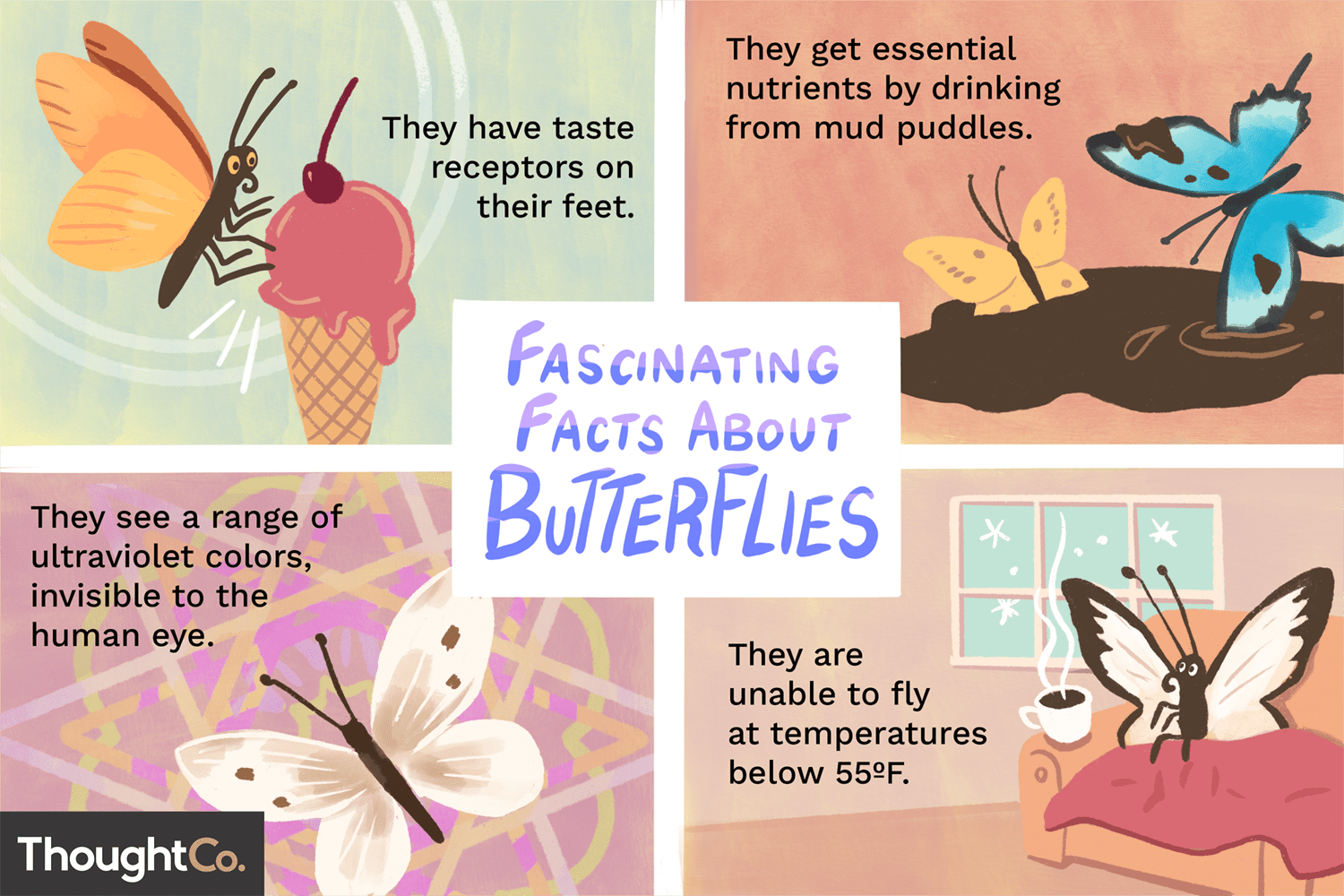
One of the most impressive abilities of butterflies is their exceptional sensory perception. Unlike humans, butterflies can see ultraviolet light, opening up a world of colors and patterns invisible to our eyes. This ultraviolet vision plays a crucial role in their communication and mate selection, as many butterfly wings display intricate UV patterns that serve as visual signals to potential partners.Perhaps even more surprising is the butterfly’s ability to taste with its feet. Equipped with chemoreceptors on their legs, butterflies can detect the chemical composition of surfaces they land on. This unique talent helps female butterflies identify suitable host plants for laying their eggs, ensuring their offspring will have an adequate food source upon hatching.

How do butterflies use mimicry to defend themselves
Butterflies employ a variety of mimicry strategies as defense mechanisms to protect themselves from predators. These strategies include Batesian mimicry, Müllerian mimicry, and other unique forms of mimicry that enhance their survival. Here is an in-depth look at how butterflies use mimicry for defense:
Batesian Mimicry
Batesian mimicry occurs when a harmless species evolves to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species. This type of mimicry is named after the British naturalist Henry Walter Bates, who first described it. In butterflies, Batesian mimicry is a common and effective defense strategy.
Monarch and Viceroy Butterflies
One of the most well-known examples of Batesian mimicry involves the Monarch and Viceroy butterflies. Monarch butterflies are toxic to many predators due to the cardiac glycosides they ingest from milkweed plants during their larval stage. Their bright orange and black coloration serves as a warning signal to predators. The Viceroy butterfly, which is not toxic, has evolved to closely resemble the Monarch in both color and pattern. This resemblance fools predators into avoiding the Viceroy, thinking it is also toxic.
Papilio Species
In the genus Papilio, female butterflies often exhibit mimetic patterns that resemble toxic species, while males do not. This sexual dimorphism is thought to arise due to the greater predatory pressure on females, which have slower flight and more predictable behavior as they stay near their host plants.
Müllerian Mimicry
Müllerian mimicry, named after the German biologist Fritz Müller, involves two or more unpalatable or toxic species evolving to resemble each other. This mutual resemblance reinforces the avoidance behavior in predators, as they learn to associate the shared warning signals with a bad taste or toxicity more quickly.
Heliconius Butterflies
Heliconius butterflies are a classic example of Müllerian mimicry. Multiple species within this genus share similar warning color patterns, such as black, red, and yellow markings. These patterns signal their unpalatability to predators, and the shared appearance helps reduce the learning curve for predators, thereby providing mutual protection to all mimetic species involved.
Mimicry Rings
In some ecosystems, butterflies form mimicry rings, where several species, both toxic and non-toxic, converge on a similar warning pattern. These rings can vary within different parts of a habitat, such as different areas of a forest or at different heights above the ground. For example, in the Amazon rainforest, clearwing butterflies form multiple mimicry rings, each adapted to specific predator distributions and environmental conditions.
Unique Mimicry Strategies
Gray Hairstreak Butterfly
The gray hairstreak butterfly employs a unique form of mimicry where its non-vital hind wing mimics the vital head. This pattern includes twin tails that resemble antennae, tricking predators into attacking the less critical part of its body. This deception increases the butterfly’s chances of survival even if it is attacked.
Clearwing Butterflies
Clearwing butterflies, such as Ithomia agnosia, participate in mimicry rings where multiple species share similar transparent or partially transparent wing patterns. These patterns help them blend into their surroundings and signal their unpalatability to predators. The diversity in mimicry patterns among clearwing butterflies is maintained by the distribution of different predator species within their habitat.
Butterflies have evolved a range of mimicry strategies to defend themselves from predators. Batesian mimicry allows harmless species to gain protection by imitating toxic species, as seen in the Monarch and Viceroy butterflies. Müllerian mimicry provides mutual protection for multiple unpalatable species, exemplified by Heliconius butterflies. Additionally, unique mimicry strategies, such as those employed by the gray hairstreak butterfly and clearwing butterflies, showcase the incredible adaptability and evolutionary ingenuity of these insects.By understanding these mimicry mechanisms, we gain insight into the complex interactions between predators and prey and the evolutionary pressures that shape the natural world. Butterflies, with their diverse and sophisticated defense strategies, continue to be a source of fascination and inspiration in the study of evolutionary biology.
Masters of Metamorphosis
The butterfly’s life cycle is a testament to nature’s transformative powers. These insects undergo complete metamorphosis, a process that involves four distinct stages:
- Egg
- Larva (caterpillar)
- Pupa (chrysalis)
- Adult butterfly
This remarkable transformation allows butterflies to adapt to different ecological niches throughout their lifespan. As caterpillars, they focus on consuming vegetation and growing, while adult butterflies prioritize reproduction and pollination.
Winged Wonders
Butterfly wings are marvels of natural engineering. Contrary to popular belief, their wings are actually transparent. The vibrant colors and patterns we observe result from thousands of tiny scales covering the wing membrane. These scales not only create stunning visual displays but also serve practical purposes:
- Camouflage: Some species can blend seamlessly into their surroundings, evading predators.
- Mimicry: Certain butterflies mimic the appearance of toxic species, deterring potential predators.
- Thermoregulation: Dark-colored scales help butterflies absorb heat, allowing them to fly in cooler temperatures.

Navigation and Migration
Some butterfly species, most notably the Monarch, undertake incredible migratory journeys spanning thousands of miles. These insects possess an innate ability to navigate using a combination of:
- Sun compass orientation
- Earth’s magnetic field detection
- Visual landmarks
What makes this feat even more astounding is that the migration often spans multiple generations, with offspring continuing the journey their parents began.
Ecological Importance
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, butterflies play crucial roles in ecosystems:
- Pollination: As they feed on nectar, butterflies transfer pollen between plants, aiding in reproduction.
- Indicator species: Their presence or absence can signal changes in environmental health.
- Food source: Butterflies and their larvae serve as important prey for various animals.
Adaptability and Resilience
Despite their fragile appearance, butterflies demonstrate remarkable adaptability and resilience. They have evolved to thrive in diverse habitats, from tropical rainforests to arctic tundras. Some species can fly at impressive speeds, with certain skippers reaching up to 37 miles per hour.
Unique Behaviors
Butterflies exhibit several intriguing behaviors that showcase their adaptability:
- Puddling: Male butterflies often gather around mud puddles to extract essential minerals and salts.
- Basking: To regulate their body temperature, butterflies often bask in the sun with their wings spread.
- Roosting: Many species roost in groups, providing safety in numbers against predators.
Conclusion
From their ultraviolet vision and taste-sensing feet to their incredible metamorphosis and migratory abilities, butterflies possess a remarkable array of cool abilities. These insects serve as a testament to the wonders of evolution and the intricate balance of nature. As we continue to study and appreciate butterflies, we gain valuable insights into ecology, biology, and the delicate interconnectedness of our natural world.By understanding and protecting these fascinating creatures, we not only preserve their beauty for future generations but also maintain the vital ecological roles they play in our environment. The next time you spot a butterfly fluttering by, take a moment to appreciate the extraordinary abilities hidden beneath those colorful wings.
